
This article mainly explains how linux checks whether ntp is synchronized. The content of the explanation in the article is simple and clear, easy to learn and understand. Next, please follow the editor's ideas and slowly deepen, let's study and learn how linux checks whether ntp is synchronized. Sync it!
3 minutes to check: 1. Using the ntpq command, you can monitor the operation of the NTP daemon ntpd and determine its performance, syntax ntpq -p; 2. Use the ntpstat command , will report the synchronization status of the NTP daemon running on the local computer. If it is synchronized, it will return 0, if the clock is not synchronized, it will return 1; 3. Use the timedatectl command, the syntax timedatectl status, and return the result of the NTP synchronized line. The result is yes Synchronize.
NTP is used to synchronize the time of a computer client or server to another server or reference clock source. It uses UTC as the time standard. It is an application layer protocol based on the connectionless IP protocol and UDP protocol. It uses a hierarchical time distribution model. The accuracy that can be obtained depends on the accuracy of the local clock hardware and the delay of equipment and processes. strict control.
There are three commands in Linux that can be used to verify NTP synchronization.
ntpq: ntpq is a standard NTP query program.
ntpstat: Display the synchronization status of the network world.
timedatectl: This controls the system time and date in the systemd system.
Method 1: How to check NTP status using ntpq command?
The ntpq utility is used to monitor the operation of the NTP daemon, ntpd, and determine performance.
The program can be run in interactive mode or controlled with command line parameters. It prints out a list of connected peers by sending multiple queries to the server. If NTP is working properly, you will get output similar to the one below.
ntpq -p
Details:
-p: Prints a list of peers known to the server and a summary of their status.
Method 2: How to check NTP status using ntpstat command?
ntpstat will report the synchronization status of the NTP daemon (ntpd) running on the local computer. If the local system is found to be in sync with the reference time source, ntpstat will report approximate time accuracy. The ntpstat command returns three status codes depending on the NTP synchronization status. Details are as follows.
0: Returns 0 if the clock is in sync.
1: Returns 1 if the clock is out of sync.
2: Return 2 if clock status is uncertain, e.g. if ntpd is unreachable.
ntpstat
Method 3: How to check NTP status using timedatectl command?
The timedatectl command is used to query and change the system clock and its setting in the systmed system.
timedatectl or timedatectl status
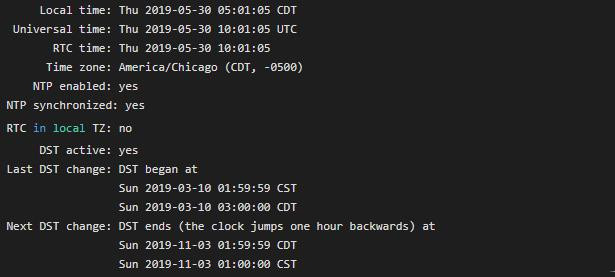
More Tips
Chrony is an NTP client replacement. It can synchronize the system clock faster and with higher time accuracy, which is especially useful for systems that are not online all the time.
chronyd is smaller, it uses less memory, and only wakes up the CPU when necessary, which saves power better. It works well even when the network is congested for extended periods of time.
You can use any of the following commands to check Chrony status.
Check Chrony tracking status.
# chronyc tracking Reference ID : C0A80105 (CentOS7.2daygeek.com) Stratum : 3 Ref time (UTC) : Thu Mar 28 05:57:27 2019 System time : 0.000002545 seconds slow of NTP time Last offset : +0.001194361 seconds RMS offset : 0.001194361 seconds Frequency : 1.650 ppm fast Residual freq : +184.101 ppm Skew : 2.962 ppm Root delay : 0.107966967 seconds Root dispersion : 1.060455322 seconds Update interval : 2.0 seconds Leap status : Normal
Run the sources command to display information about the current time source.
# chronyc sources 210 Number of sources = 1 MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample ============= =============================== ^* CentOS7.2daygeek.com 2 6 17 62 +36us[+1230us] +/- 1111ms
Copyright Description:No reproduction without permission。

Knowledge sharing community for developers。
Let more developers benefit from it。
Help developers share knowledge through the Internet。
Follow us